How Solar Panels Are Made: Complete Homeowner-Friendly Guide
You’re not the only one who has ever wondered how solar panels made. With solar power emerging as one of Australia’s fastest-growing energy choices, many householders are curious about how these powerful, energy-saving systems are created. Knowing how the process works doesn’t simply satisfy your curiosity; it also helps you choose the best solar panels for your home.
We will show you how to make solar panels in a simple, transparent, and easy-to-understand approach in this article. We’ll also talk about the materials used, the technology behind the manufacture, quality inspections, and why it’s important to use respected installers.
Let’s get started.
Get a Free Solar Quotes
What Are Solar Panels? A Quick Overview
It helps to know how solar panels made, you learn how they are created.
Solar panels, or photovoltaic (PV) panels, use semiconductor materials, mostly silicon, to convert sunlight into electricity. There are many types of these panels (monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film), but the basic way they are made is the same.
Each solar panel contains:
- Silicon cells
- Glass cover
- EVA encapsulation layers
- Aluminium frame
- Backsheet
- Junction box
Now let’s break down exactly how solar panels made at the factory level.
Step 1: Extracting and Purifying Silicon
Silicon, the second most common material on Earth, is where the story of how solar panels made begins. A high-heat industrial method takes silicon out of quartz rock.
Purification Process
Silicon has to be extremely pure for solar panels. Manufacturers heat the raw silicon to very high temperatures until the impurities burn away. This makes the silicon more than 99% pure.
The better the solar cell works, the cleaner it is.
Step 2: Creating Silicon Ingots
Once purified, the silicon is turned into large solid blocks called ingots. These are created using one of two major manufacturing techniques:
Monocrystalline Ingots
Molten silicon is shaped into a single crystal structure. This results in:
- Higher efficiency
- Better performance in low-light
- A uniform black appearance
Polycrystalline Ingots
Molten silicon is poured into a mold and allowed to cool naturally. This forms multiple crystal structures, giving it:
- Lower cost
- Slightly lower efficiency
- Blue, speckled appearance
Both processes are important when explaining how solar panels made, as they define the final panel type.
Step 3: Slicing Wafers
Next comes wafering — a crucial step in how solar panels made.
Manufacturers slice the silicon ingots using precision wire saws into extremely thin wafers (about the thickness of a sheet of paper). These wafers must be:
- Smooth
- Durable
- Thin enough for sunlight absorption but thick enough for electrical conduction
After slicing, wafers undergo polishing to remove damage from the saw wires.
Step 4: Turning Wafers Into Solar Cells
This is where the real transformation happens in how solar panels made.
Doping – Adding Electrical Properties
Silicon wafers alone cannot produce electricity. They must be treated to create a positive (p-type) and negative (n-type) layer.
This is achieved by adding elements such as:
- Phosphorus for negative charge
- Boron for positive charge
This creates a PN junction, the heart of electricity generation.
Applying Anti-Reflective Coating
Silicon reflects sunlight naturally, which reduces efficiency.
So, manufacturers apply an anti-reflective coating that:
- Reduces glare
- Increases sunlight absorption
- Gives cells their signature blue or black colour
Metal Contacts
There are thin metal lines (busbars and fingers) printed on each cell. They gather and move the electricity that has been made.
These finished solar cells move on to the panel construction stage when they are ready.
Step 5: Assembling Solar Cells Into a Panel
Solar cells are arranged into a structured grid — often 60-cell or 72-cell panels.
Cell Stringing
Metal ribbons are used by machines to solder solar cells together to make strings. To make sure maximum efficiency, you need to be precise.
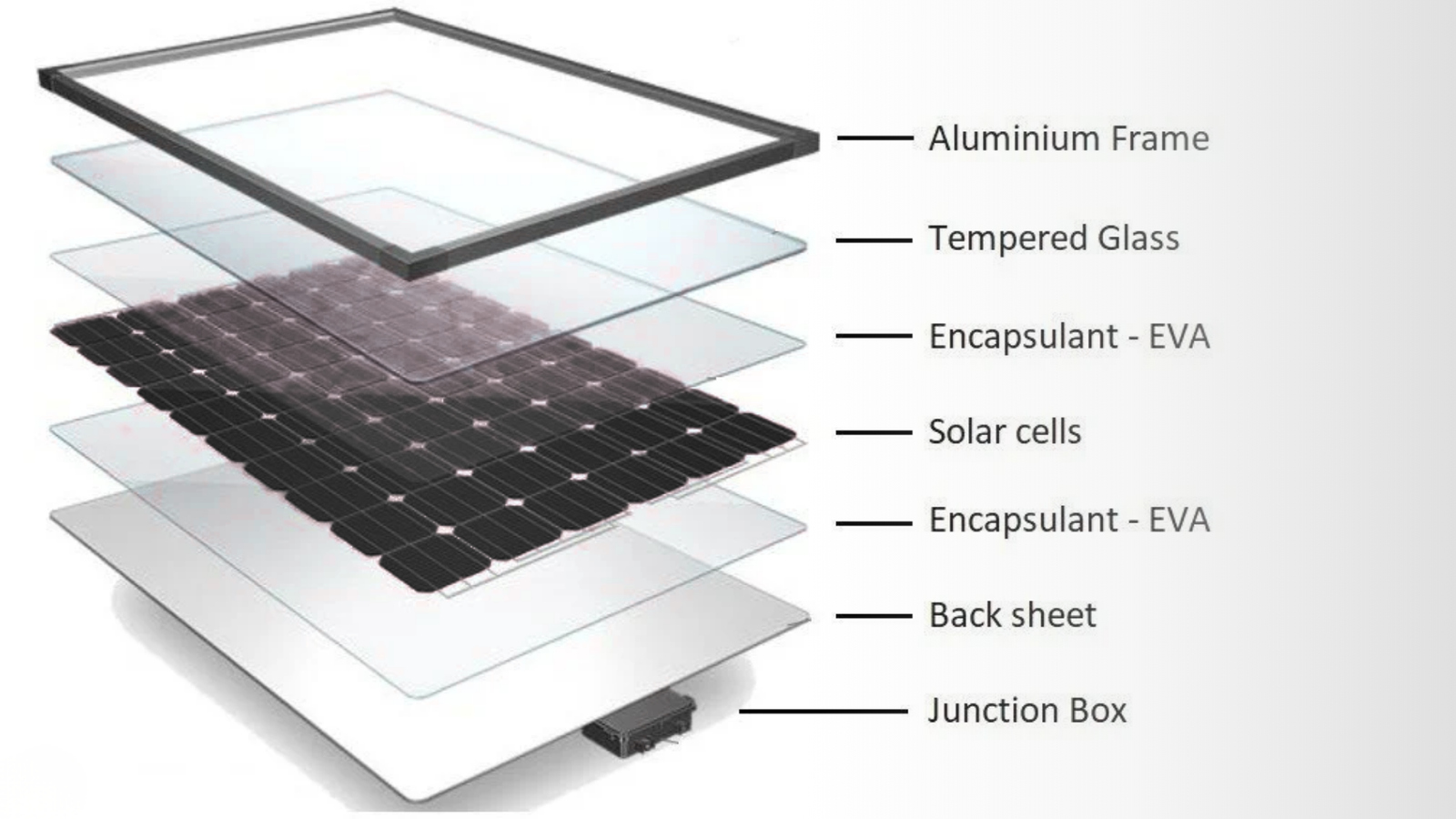
Layering (Encapsulation)
Understanding encapsulation is key for explaining how solar panels made.
A typical solar panel layer stack:
- Tempered glass (front)
- EVA sheet
- Solar cell layer
- EVA sheet
- Backsheet
This sandwich structure protects the delicate cells from heat, moisture, and impact.
Step 6: Laminating the Panel
The layer stack enters a vacuum laminator.
Inside, the EVA melts and bonds everything together tightly.
This step:
- Removes all trapped air
- Seals the panel
- Ensures long-term durability
It’s one of the most important steps in how solar panels made.
Step 7: Adding the Aluminium Frame
The aluminium frame provides:
- Strength
- Easy mounting
- Extra protection in extreme weather (very important in Australia!)
Frames are typically anodised to resist rust and corrosion.
Step 8: Installing the Junction Box
The junction box is fixed at the back of the panel and contains bypass diodes that prevent power loss if part of the panel is shaded.
Wiring is sealed to ensure waterproof performance.
Step 9: Testing and Quality Check
No explanation of how solar panels made is complete without discussing testing.
Manufacturers perform:
- EL (Electroluminescence) testing
- Flash testing (performance rating)
- Thermal cycling tests
- Mechanical load tests
These ensure the panel can withstand:
- UV exposure
- High heat
- Cold temperatures
- Hail
- Wind loads
Quality control ensures customers get panels that last 25–30 years or more.
Step 10: Packaging and Shipping
Finally, the panels are cleaned, labelled, and packed for transport.
From here, they head to distributors, installers, and your roof!
Why Knowing How Solar Panels Are Made Matters
Understanding how solar panels made helps you:
- Choose better-quality brands
- Identify differences between cheap vs premium panels
- Make smarter long-term investments
- Appreciate the technology powering your home
For Australian homeowners, this knowledge is even more valuable — our climate demands durable, high-efficiency panels.
Common Materials Used in Solar Panel Manufacturing
To give a clearer idea of how solar panels made, here are the primary materials:
- Silicon – main semiconductor
- Tempered glass – protects the cells
- EVA (ethylene vinyl acetate) – encapsulation
- Backsheet polymers – weather protection
- Aluminium frame – durability
- Copper wiring – electrical flow
- Junction box + bypass diodes – safety and performance
High-quality materials = long-lasting solar performance.
Benefits of High-Quality Manufacturing
When the process of how solar panels made is done with precision, you get:
- Better efficiency
- Longer lifespan
- Reduced degradation rate
- Better performance in heat
- Stronger warranty
This is why choosing solar panels from reputable brands and trusted installers like Electrical Masters matters.
Conclusion
Understanding how solar panels made helps you understand the wonderful innovation that is on your roof. Every operation, from getting silicon out of the ground to making cells and putting panels together, is meant to get the best performance, durability, and efficiency.
Always choose high-quality solar panels and professional installers like The Solar King to get the most out of your investment.
Contact: The Solar King now to get free quote.
